Unveiling the Enigmatic Ehrenstein Illusion: A Visual Marvel of Perception
The Fascinating Ehrenstein Illusion
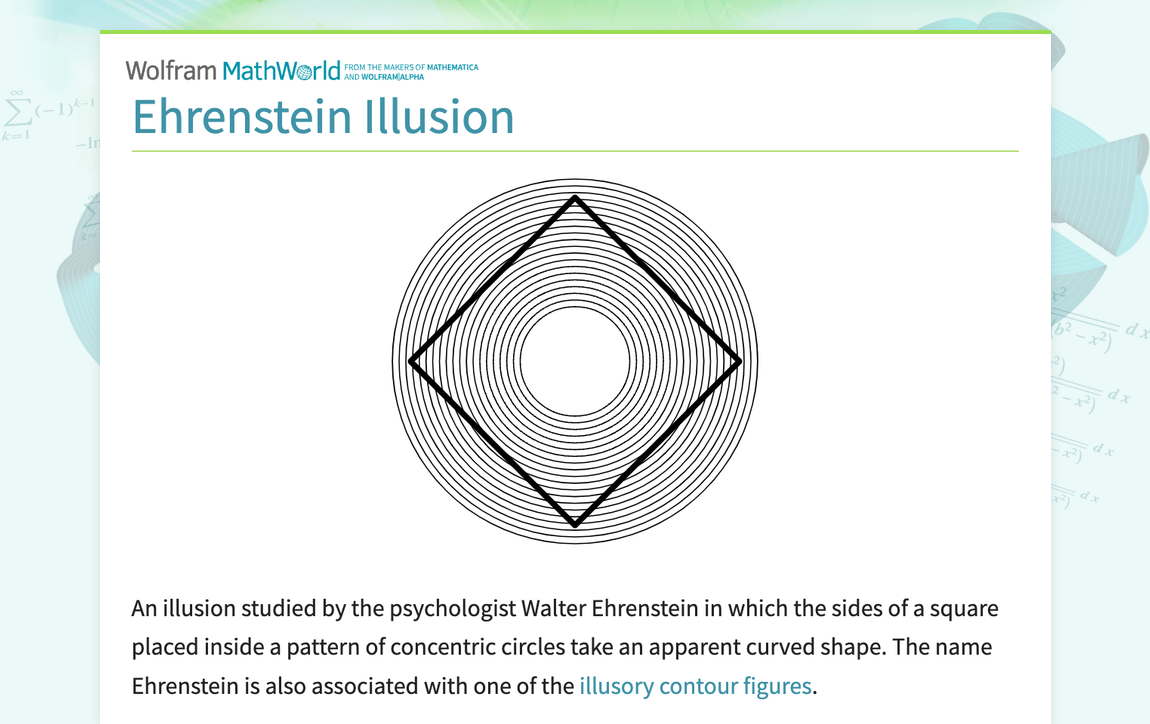
The Ehrenstein illusion is a captivating visual phenomenon that plays tricks on our perception. Named after the German psychologist Walter Ehrenstein, this optical illusion involves concentric circles with radial lines extending outwards from the centre.
When viewing the Ehrenstein illusion, observers often perceive illusory grey or dark spots at the intersections of the radial lines and the circles. These phantom shapes seem to appear and disappear as one gazes at the image, creating a mesmerising effect that challenges our understanding of reality.
Researchers believe that the Ehrenstein illusion occurs due to the way our brain processes visual information. The intricate patterns and contrasting colours in the illusion can confuse our neural pathways, leading to misinterpretations of depth and shape.
Despite its simple design, the Ehrenstein illusion continues to intrigue scientists and artists alike. Its ability to distort perception highlights the complex nature of human vision and cognition, demonstrating how easily our minds can be deceived by cleverly crafted visual stimuli.
Next time you encounter an optical illusion like the Ehrenstein effect, take a moment to appreciate the wonders of human perception and how easily our senses can be manipulated by clever illusions.
Exploring Optical Illusions: Understanding the Ehrenstein and Other Visual Phenomena
- What is the biggest illusion in the world?
- Is the Ebbinghaus illusion real?
- How does the Ehrenstein illusion work?
- What is an example of an illusion in schizophrenia?
- What is the Ebbinghaus illusion theory?
- How to explain Müller-Lyer illusion?
- What is the most famous optical illusion?
- What is the Zollner illusion explained?
What is the biggest illusion in the world?
When it comes to optical illusions, the concept of “biggest” can be subjective and open to interpretation. However, one frequently discussed illusion that captivates many is the Ehrenstein illusion. This visual phenomenon, characterised by its intricate patterns and deceptive shapes, challenges our perception in a profound way. While some may argue that the biggest illusion in the world lies in the vastness of the universe or the complexities of human consciousness, the Ehrenstein illusion serves as a reminder of how easily our minds can be tricked by cleverly designed visual stimuli.
Is the Ebbinghaus illusion real?
The Ebbinghaus illusion, also known as the Titchener circles, is indeed a real and well-documented optical phenomenon that influences our perception of relative size. Named after the German psychologist Hermann Ebbinghaus, this visual illusion involves two identical central circles surrounded by different-sized circles. Despite the central circles being the same size, they appear to be different due to the context provided by the surrounding circles. This distortion in perception sheds light on how our brains process visual information and can lead to fascinating insights into human cognition and visual processing mechanisms.
How does the Ehrenstein illusion work?
The Ehrenstein illusion captivates viewers by creating illusory grey or dark spots at the intersections of radial lines and concentric circles, prompting the frequently asked question: “How does the Ehrenstein illusion work?” This optical phenomenon tricks our perception due to the intricate patterns and contrasting colours in the image. As observers gaze at the illusion, their brains struggle to interpret the visual information accurately, leading to misinterpretations of depth and shape. The Ehrenstein illusion showcases how easily our neural pathways can be confused by cleverly designed visual stimuli, highlighting the fascinating complexities of human vision and cognition.
What is an example of an illusion in schizophrenia?
In the context of schizophrenia, individuals may experience various types of perceptual disturbances, including visual illusions. One example of an illusion commonly reported in schizophrenia is known as the “size-weight illusion.” This phenomenon involves perceiving two objects of equal weight but different sizes as having different weights. People with schizophrenia may exhibit altered sensory processing, leading to distortions in their perception of physical attributes such as size and weight. Understanding how these illusions manifest in individuals with schizophrenia can provide valuable insights into the complex interplay between perception, cognition, and mental health.
What is the Ebbinghaus illusion theory?
The Ebbinghaus illusion, also known as the Titchener circles, is a visual phenomenon that explores how our perception of an object’s size can be influenced by the surrounding context. In this illusion, two identical central circles are surrounded by different-sized circles. Despite being the same size, the central circles appear to be different sizes due to the context provided by the surrounding circles. This optical illusion challenges our understanding of relative size perception and highlights how our brains can be easily deceived by contextual cues. Researchers continue to study the Ebbinghaus illusion to gain insights into how our visual system processes and interprets spatial information.
How to explain Müller-Lyer illusion?
The Müller-Lyer illusion is a classic visual phenomenon that puzzles many observers. This optical illusion consists of two lines of equal length, each adorned with arrow-like fins pointing inwards or outwards. Despite the lines being the same length, the addition of the fins creates an illusion of one line appearing longer than the other. Psychologists explain this discrepancy in perception as a result of our brain’s tendency to interpret depth and distance cues in the context of familiar geometric shapes. The Müller-Lyer illusion showcases how our visual system can be influenced by contextual clues, leading to misjudgements in size and length perception.
What is the most famous optical illusion?
One of the most frequently asked questions in the realm of optical illusions is, “What is the most famous optical illusion?” While there are many iconic illusions that have captured the public’s imagination over the years, one standout contender for the title of the most famous optical illusion is the Müller-Lyer illusion. This classic visual phenomenon involves two lines of equal length with arrow-like tails pointing in opposite directions, creating an illusion of one line appearing longer than the other. The Müller-Lyer illusion has fascinated researchers and enthusiasts alike for decades, serving as a testament to the power of perception and how easily our minds can be deceived by cleverly designed visual stimuli.
What is the Zollner illusion explained?
The Zollner illusion is another intriguing visual phenomenon that deceives our perception in a captivating way. Named after the German astrophysicist and psychologist Johann Karl Friedrich Zollner, this optical illusion involves a series of parallel lines intersected by diagonal lines. When observing the Zollner illusion, viewers often perceive the parallel lines as being misaligned or distorted, creating an illusion of depth or movement. This fascinating effect challenges our understanding of geometric shapes and spatial relationships, showcasing the intricate ways in which our brains interpret visual information.